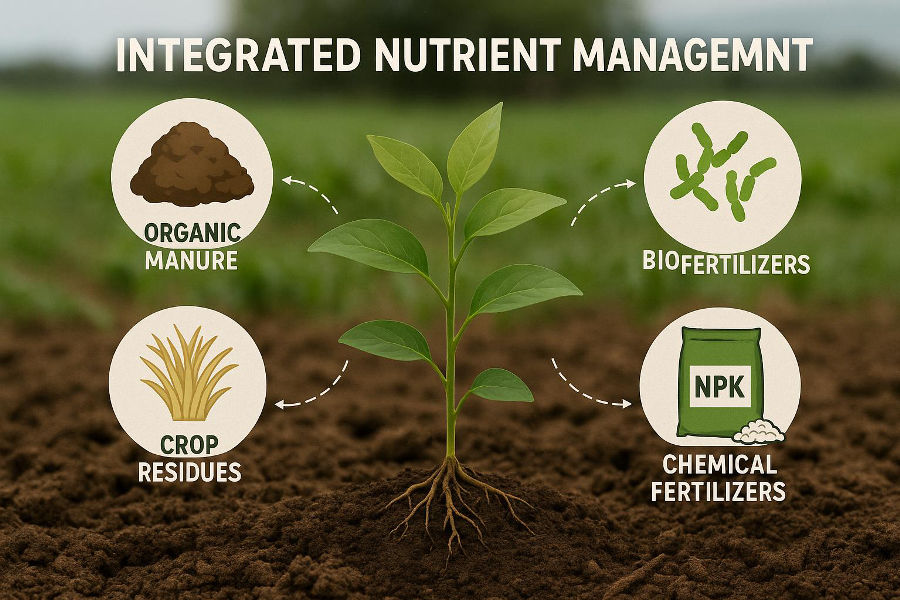
Integrated Nutrient Management (INM): A Sustainable Approach to Crop Nutrition
Integrated Nutrient Management, commonly known as INM, is a scientifically proven strategy to supply crops with the right balance of nutrients while maintaining long-term soil health. It combines chemical fertilizers, organic manures, and biofertilizers to ensure efficient and eco-friendly nutrient delivery to plants.
What is INM?
INM is the judicious and balanced use of different nutrient sources:
-
Chemical fertilizers for immediate nutrient availability
-
Organic manures like farmyard manure (FYM), compost, and green manures for improving soil structure
-
Biofertilizers like Rhizobium, Azotobacter, and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria that support natural nutrient cycling
This combination helps maintain soil fertility and improve crop yields without degrading the environment.
Why is INM Important?
-
Maintains and improves soil fertility
-
Reduces over-reliance on chemical fertilizers
-
Increases nutrient use efficiency
-
Enhances microbial activity and soil biodiversity
-
Promotes sustainable crop production
Key Components of INM
-
Chemical Fertilizers: Provide quick and targeted nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
-
Organic Sources: Compost, vermicompost, green manure, and crop residues contribute to organic carbon and micronutrients.
-
Biofertilizers: Living microorganisms that fix nitrogen, solubilize phosphorus, and stimulate plant growth.
Practical Example
In sugarcane farming, a farmer might use:
-
60 percent of the recommended nitrogen through urea
-
20 percent through well-decomposed compost
-
20 percent through Azotobacter biofertilizer
This ensures continuous and balanced nutrient availability throughout the crop cycle.