Acidic Soils and Their Reclamation
To achieve good crop productivity, maintaining a balanced soil pH is extremely important. In many regions, one of the major reasons for low crop yield is acidic soil. With proper understanding and scientific management, even acidic soils can be made productive.
What Are Acidic Soils
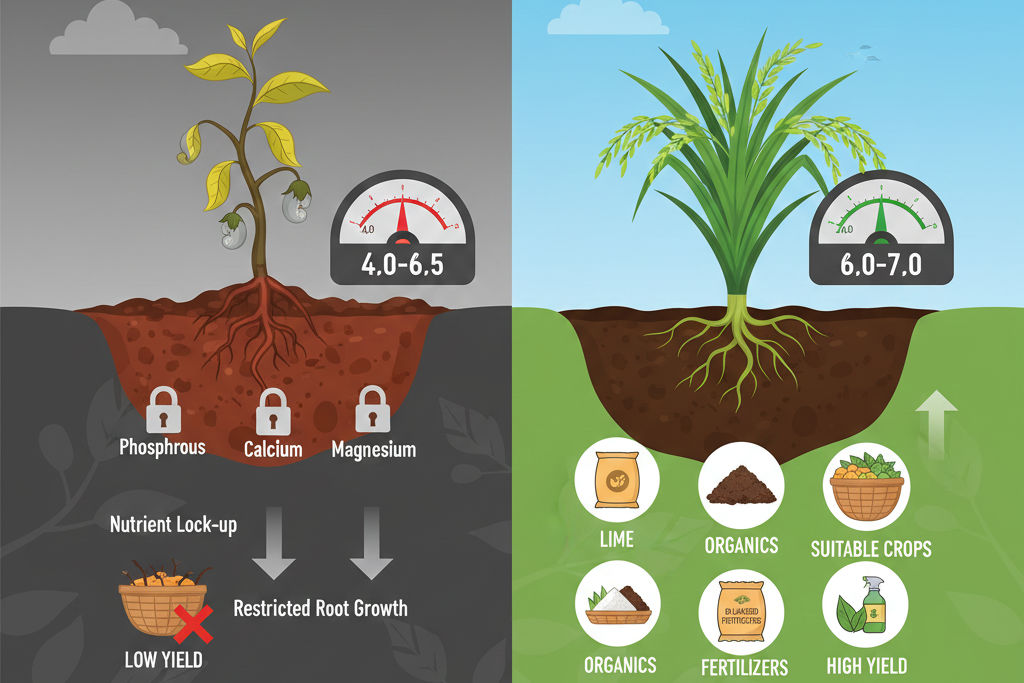
Soils having a pH value below 6.5 are classified as acidic soils. In India, such soils are commonly found in Kerala, the Konkan belt, the Western Ghats, and high-rainfall regions. These soils are mostly Laterite soils.
Characteristics of Acidic Soils
In acidic soils, iron and aluminum remain highly active. As a result:
-
Availability of phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium decreases
-
Root growth is restricted
-
Overall crop growth is stunted
-
Crop yield is adversely affected
Major Causes of Soil Acidity
-
Leaching of basic nutrients like calcium and magnesium due to heavy rainfall
-
Excessive use of sulfate and nitrate-based fertilizers
-
Continuous use of chemical fertilizers
-
Low organic matter content in soil
Measures to Reclaim Acidic Soils
1) Application of Lime
Use of lime, dolomite, or calcium carbonate based on soil testing is the most effective solution. It increases soil pH, reduces aluminum toxicity, and improves nutrient availability.
2) Use of Organic Matter
Regular application of farmyard manure, compost, green manure, and vermicompost enhances biological activity in the soil and gradually reduces acidity.
3) Balanced Fertilizer Management
Avoid excessive use of acid-forming fertilizers such as ammonium sulfate. Fertilizer application should always be based on soil test recommendations.
4) Selection of Suitable Crops
Crops like rice, cashew, pineapple, tea, and spices perform better in acidic soils.
Conclusion
Acidic soil does not mean infertile soil. With soil testing, proper reclamation practices, and sustainable management, acidic soils can become highly productive. Understanding soil health and managing it scientifically is the key to sustainable and profitable agriculture.