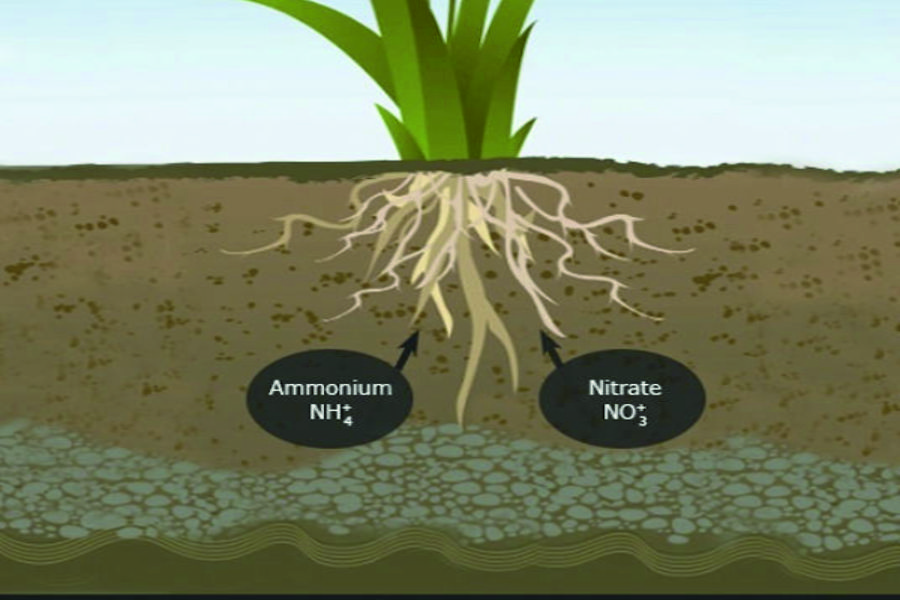
Nitrogen is a crucial nutrient for plant growth, playing a vital role in chlorophyll formation, protein synthesis, and overall development. However, plants cannot directly absorb atmospheric nitrogen (N₂). Instead, they take up nitrogen in specific forms from the soil and fertilizers. Major Forms of Nitrogen Absorbed by Plants Nitrate (NO₃⁻): The most readily available form of nitrogen for plants. Easily absorbed by roots and transported throughout the plant. Promotes quick growth and greener foliage. Ammonium (NH₄⁺): Another primary form of nitrogen uptake. Less mobile than nitrate but efficiently utilized by plants. Helps in root development and stress tolerance. Urea (CO(NH₂)₂): A widely used nitrogen fertilizer. Converted into ammonium (NH₄⁺) in the soil before plant uptake. Enhances vegetative growth and yield. Organic Nitrogen: Derived from decomposed plant and animal matter. Slowly mineralized into ammonium and nitrate by soil microbes. Improves long-term soil fertility. Importance of Nitrogen Forms in Agriculture Balanced Fertilization: Proper application of NO₃⁻ and NH₄⁺ improves crop productivity. Efficient Nutrient Management: Reduces nitrogen loss through leaching and volatilization. Sustainable Farming: Using organic sources and biofertilizers enhances soil health.